Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Common Administration Tasks
The following sections are examples of common tasks a user may perform to administer and maintain a Lightbits product. These tasks are simply management commands grouped into a specific sequence with brief explanations to put the commands into context.
All commands and output are examples only and the specific values should not be used when performing similar tasks on your own Lightbits storage server or application server.
Lightbits recommends that you use these examples to help you build your own commands. Be sure to refer to the latest API User Manual when creating your commands to ensure that you are using the latest syntax as defined by the product version you are managing.
JWT
JWT, or JSON Web Token, is an open standard to securely transmit data between parties as a JSON object. We use JWT in the Lightbits SDS for all API calls (lbcli and REST/GRPC). By default the cluster will be created with a system JWT (Cluster Admin) and a default JWT that is associated with the default project Admin (can only do project level APIs on the default project). If you create more projects/tenants, you will have additional Admin JWTs for each project.
The JWT can be found either in the deployment folder (Example 1 below) within your S3 deployment bucket (this is the S3 bucket provided as ‘S3ConfBucketName’ parameter), or within one of the storage instances (Example 2 below).
Example 1: The following is an example of the folder content from the AWS S3 console:
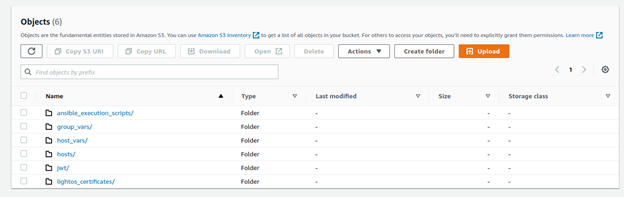
Within this folder you can see the subfolder jwt/, which includes the ‘system_jwt’:
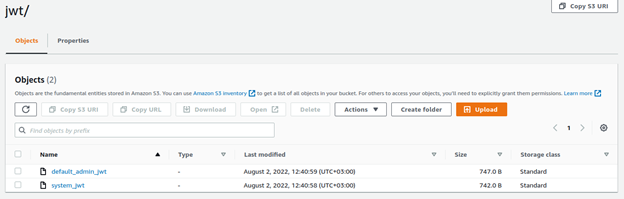
Example 2: The generated JWT is also located in /opt/lightbits-app/config/cluster1 within each storage instance.
In order to connect to a storage instance, go to the EC2 instances dashboard and select one of the lightbits-node instances. Then click Connect > Session Manager.
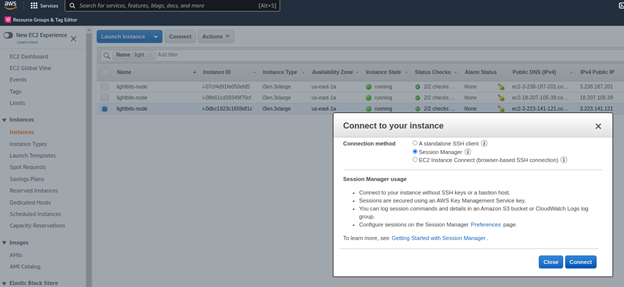
Within the session manager (SSH) window:
The system JWT can be found under:
$ cd /opt/light-app/config/cluster1/; . system_jwt;It is recommended to save the system_jwt as an environment variable, so that it can be easily added to any lbcli or API command.
For example:
lbcli list nodes -J $LIGHTOS_JWTYou can also save the JWT in the lbcli configuration YAML file /etc/lbcli/lbcli.yaml. This allows you to perform further lbcli management commands to the storage cluster without specifying the JWT in each command.
For example:
lbcli list nodes -J $LIGHTOS_JWTName UUID State NVMe endpoint Failure domains Local rebuild progressip-10-240-99-56.ec2.internal-0 1c221509-be0c-57f9-9f66-980174d8f91a Active 10.240.99.56:4420 [i-020acc69e738c6c39 ip-1...] Noneip-10-240-99-224.ec2.internal-0 83bb07d7-2bb8-5e8e-a3db-fce76288b971 Active 10.240.99.224:4420 [i-04896c6c251c859b1 ip-1...] Noneip-10-240-99-148.ec2.internal-0 ad122562-be10-5268-82d0-7fa41349f9f7 Active 10.240.99.148:4420 [i-017209734ebc14b03 ip-1...] NoneSave the > vi /etc/lbcli/lbcli.yamloutput-format: human-readable dial-timeout: 5s command-timeout: 60s insecure-skip-tls-verify: true debug: false api-version: 2 insecure-transport: false endpoint: https://127.0.0.1:443 jwt: <the JWT you copied>Once you have the JWT, you can start working on the lbcli or Lightbits APIs to create volumes and start mounting them on your clients.
© 2026 Lightbits Labs™