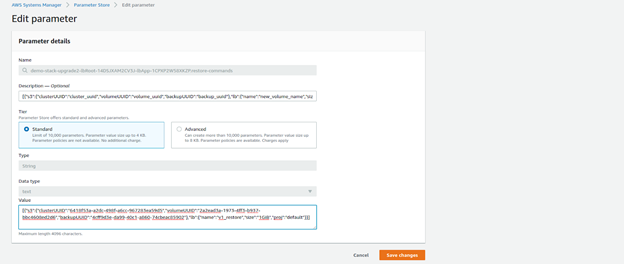
A restore process is specific to a certain backup taken at a certain time. The restore is initiated in this version by saving the restore configuration as a parameter in the AWS Parameter Store. Once the restore is triggered, the backup importer will create a new volume and copy all the data from the relevant backup to the volume.
Once restore is done you should update the ACL of the restored volume, to give access to any client (ACL=ALLOW_ANY), or to limit access to the volume to specific clients. This should only be done after you verify in the Lambda log that the Restore is finished. Once restore is done the “auto_ restore” string in the ACL can be removed and you can configure the ACL as required. Note once the “auto_restore” flag is removed from the ACL it will be backed up as any other Available volume in the cluster.
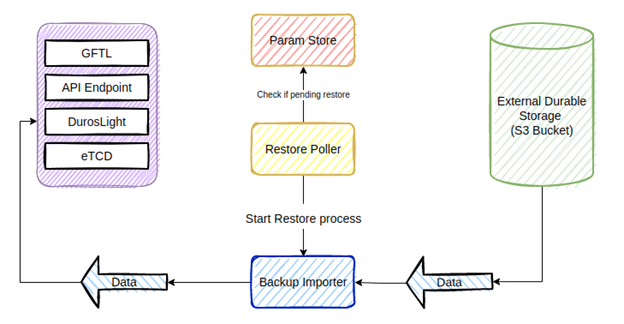
Before triggering the restore, collect the following information:
- ClusterUUID: This can be taken from the Lightbits get cluster info API (put the link to get cluster info API), or it can be found in the root of the backup repo in S3.
- VolumeUUID: This is the UUID of the volume that you want to restore. Note that the restore command will not affect the existing volume but instead will restore onto a new volume. If the cluster and volume exist, the Volume UUID can be found using the Lightbits get volume or list volumes API. If the cluster or volume do not exist, you can find the volume name and UUID in the backup repo in S3. You will need to list all the folders under the cluster UUID backup folder. Each folder holds the UUID_volumeName.
- BackupUUID: Can be found in S3 under the clusterUUID folder → VolumeUUID folder. There will be a list of folders, with each representing a different backup UUID. Each backup UUID should be from a different date. Use the backup UUID from the date that is needed to restore from.
- Name: The new volume name to give to the restored volume. The restore does not “Restore in place” and will not overwrite the existing volume, but instead will create a new volume with the restored data.
- Size: The size of the volume to allocate for the restore.
- ProjectName: The project that the volume should be associated with.
The format of the restore command parameter should be as follows:
[{"s3":{"clusterUUID":"<clusterUUID>","volumeUUID":"<volumeUUID>","backupUUID":"<backupUUID>"},"lb":{"name":"<VolumeName>","size":"<volumeSize>","proj":"<projectName>"}}][{"s3":{"clusterUUID":"0839bc48-1f33-4ecc-bbbc-e1a72007596b","volumeUUID":"c520cb82-92e2-4171-a058-3aaeaa8dfb93","backupUUID":"4cff9d3e-da99-40c1-a860-74cbeac85902"},"lb":{"name":"v1_restore","size":"1GiB","proj":"default"}}]- In the AWS console, go to the Parameter Store.
- Filter by restore-commands. There should be only one parameter there.
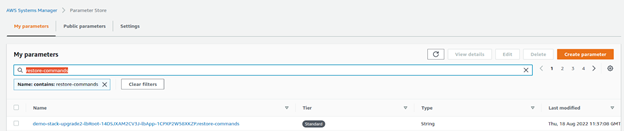
- Click the parameter and then click Edit.
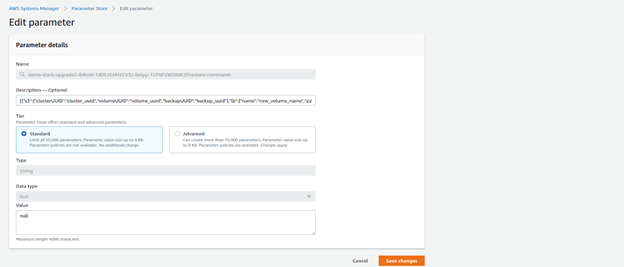
- Enter the Above String in the Value field and click Save Changes. This will trigger the restore of the required volume. Make sure to edit it correctly and that all parentheses exist. Note that this must be done for each of the volumes that need to be restored.