Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Volume Replication
Volume replication refers to data synchronously replicated to multiple storage servers. Volumes can sustain server failures. The replication also can be set up across different failure domains, which can deliver most high availability storage service.
The replication data flow is illustrated in the diagram below.
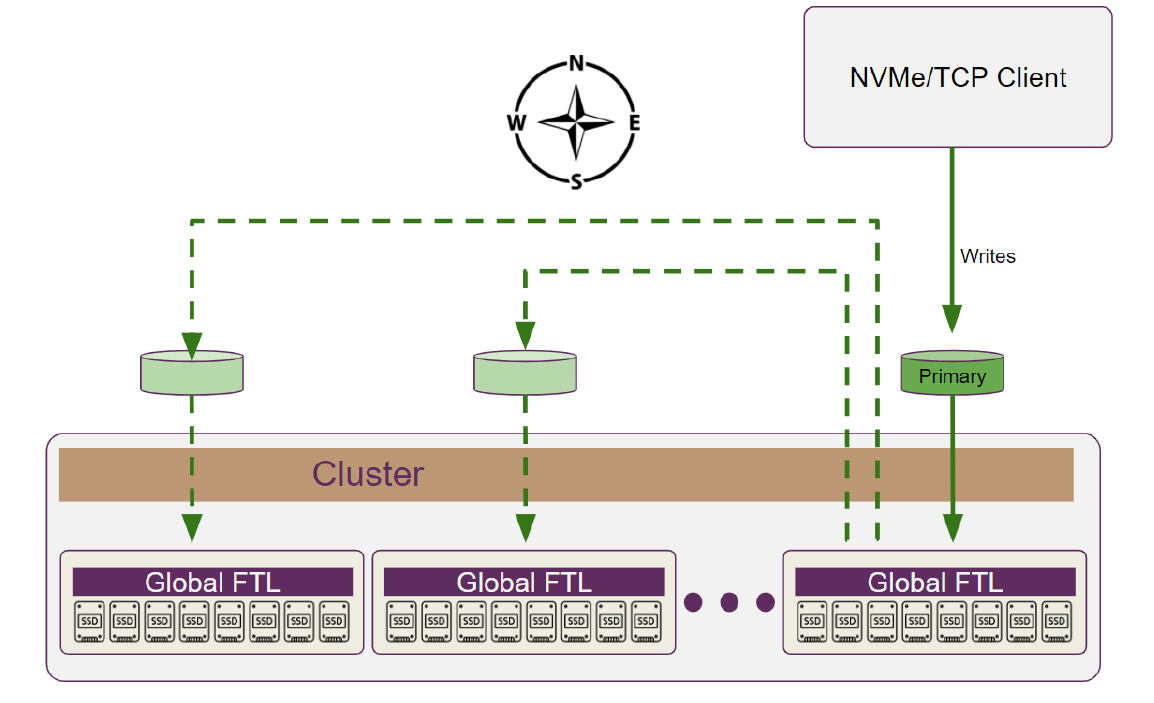
Test Purpose
Verify that the write IO data is replicated as expected, and test that different replication volumes can work in parallel.
The high availability, optimized path switchover in case of server failure will be covered in the “Server Failure Handling” test case.
Test Steps
- Create three volumes with different replication numbers: 1, 2 and 3 for Client Server A.
# For loop to create volumesfor i in {1..3}; do lbcli create volume --project-name=default --name=replica${i}-test-vol --replica-count=$i --size=100GB --acl="acl3"; done# Check volumesroot@lightos-server00:~ lbcli list volumes | grep replica -test | sortreplica1-test-vol 5354e422-5b53-48d9-98dd-6c48c9edc0c6 Available FullyProtected 9 93 GiB 1 false values:"acl3" Nonereplica2-test-vol 4f680678-3094-4795-8e98-3bee00750fe2 Available FullyProtected 12 186 GiB 2 false values:"acl3" Nonereplica3-test-vol cf0d5244-9a4e-4a88-b8e2-facfbc2aa45a Available FullyProtected 11 279 GiB 3 false values:"acl3" None- On the client server side, use the “nvme list” command to check the new volumes and the multi-path information.
# Check nvme devicesroot@client-a:~ nvme listNode SN ModelNamespace Usage Format FW Rev---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------------------------- -------------------------- ---------------- --------/dev/nvme0n1 b4649e6a3496d720 Lightbits LightOS 9100.00 GB / 100.00 GB 4 KiB + 0 B 2.3/dev/nvme0n2 b4649e6a3496d720 Lightbits LightOS 12200.00 GB / 200.00 GB 4 KiB + 0 B 2.3/dev/nvme0n3 b4649e6a3496d720 Lightbits LightOS 11300.00 GB / 300.00 GB 4 KiB + 0 B 2.3# Check controller mapping for vol1root@client-a:~ nvme list-subsys /dev/nvme0n1nvme-subsys0-NQN=nqn.2016-01.com.lightbitslabs:uuid:e7ba5876-431b-43ca-a7e5-4a0aaae3d1e1\+- nvme0 tcp traddr=10.20.130.10 trsvcid=4420 live optimized+- nvme1 tcp traddr=10.20.130.11 trsvcid=4420 live+- nvme2 tcp traddr=10.20.130.12 trsvcid=4420 live# Check controller mapping for vol2root@client-a:~ nvme list-subsys /dev/nvme0n2nvme-subsys0-NQN=nqn.2016-01.com.lightbitslabs:uuid:e7ba5876-431b-43ca-a7e5-4a0aaae3d1e1\+- nvme0 tcp traddr=10.20.130.10 trsvcid=4420 live optimized+- nvme1 tcp traddr=10.20.130.11 trsvcid=4420 live inaccessible+- nvme2 tcp traddr=10.20.130.12 trsvcid=4420 live# Check controller mapping for vol3root@client-a:~ nvme list-subsys /dev/nvme0n3nvme-subsys0-NQN=nqn.2016-01.com.lightbitslabs:uuid:e7ba5876-431b-43ca-a7e5-4a0aaae3d1e1\+- nvme0 tcp traddr=10.20.130.10 trsvcid=4420 live optimized+- nvme1 tcp traddr=10.20.130.11 trsvcid=4420 live inaccessible+- nvme2 tcp traddr=10.20.130.12 trsvcid=4420 live inaccessibleThe “live optimized” path is the primary replication resided path, while “live inaccessible” is the secondary replication resided path. The replication number of the volume can also be reflected in this multi-path information. For example, three replication volumes have three paths total.
- In the client server, use FIO to generate the write IO to these three volumes separately, and monitor the network traffic in these three Lightbits storage servers to verify whether the replication worked as expected. For example, use the Linux tool “nload” - running in the three storage servers - to monitor the data traffic.
The following is an example of a single replication volume IO traffic - with only incoming data IO in the primary path (MB or KB level traffic is the ACK or management IO).
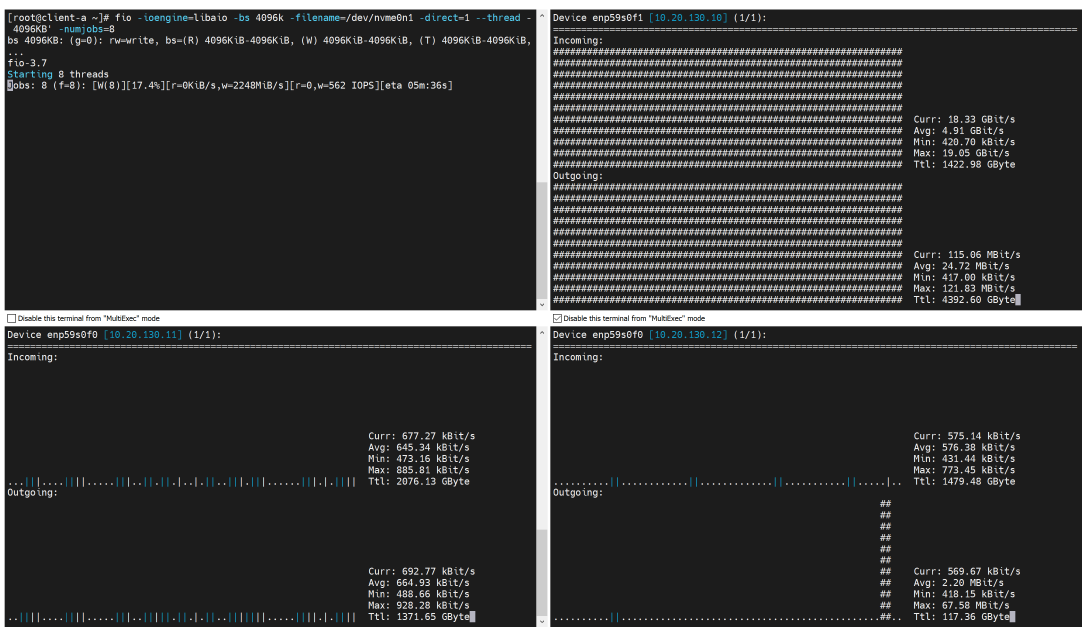
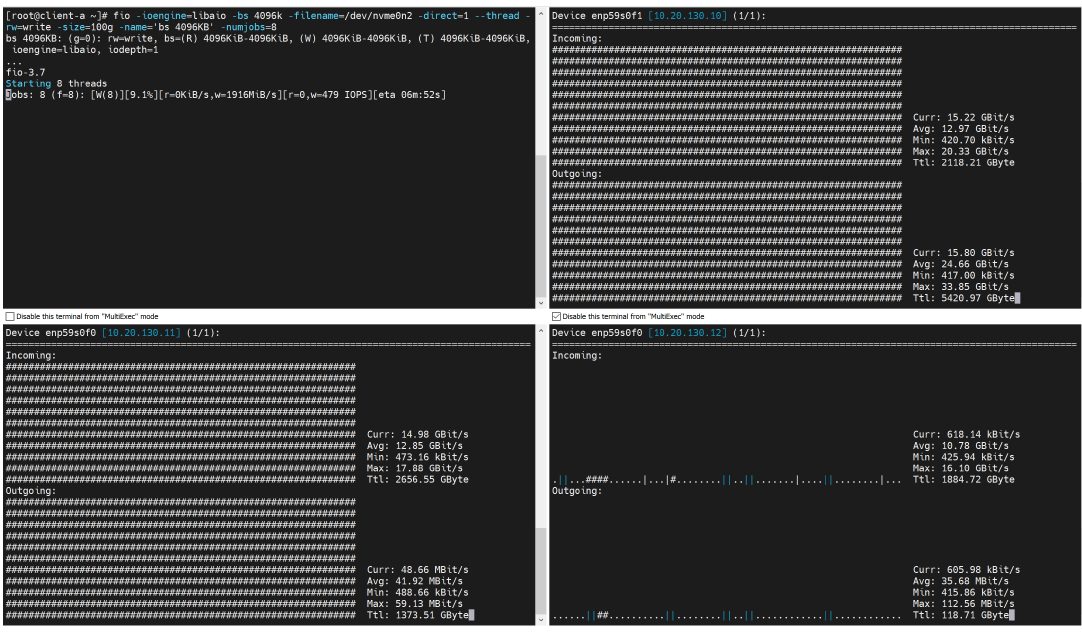
The following is an example of a two replication volume IO traffic. In the primary path, in addition to the incoming traffic, there is also the same bandwidth outgoing traffic, which is for replicated data. And in the other secondary path, there is incoming data traffic.
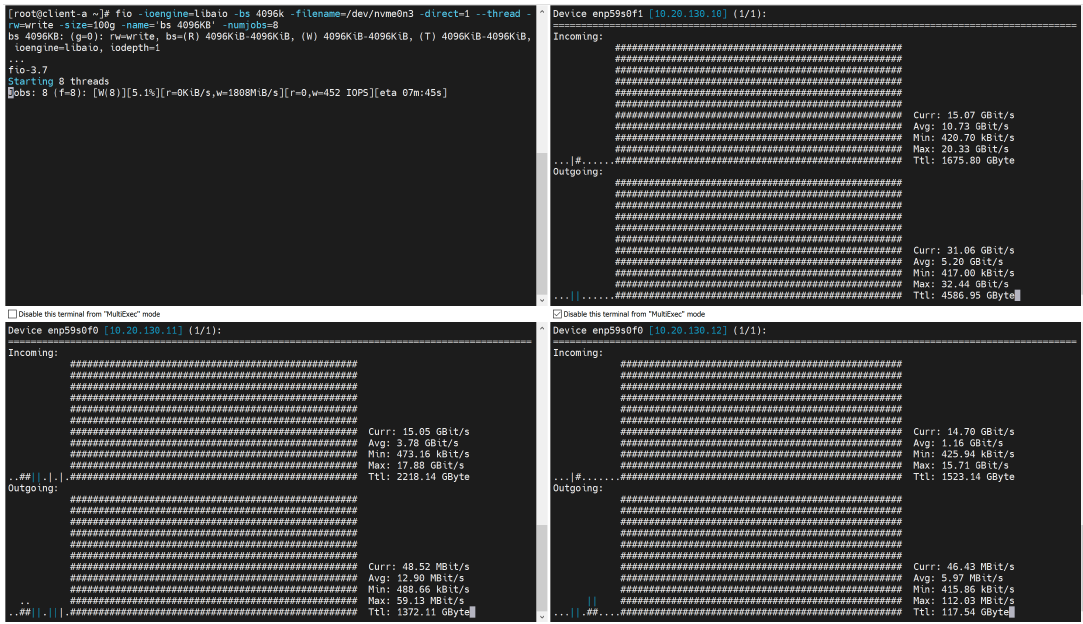
The following is an example of a three replication volume IO traffic. In the primary path, the outgoing traffic is almost double that of the incoming traffic. This is because it needs to replicate the data IO to the other two secondary paths. The two secondary paths have the same incoming traffic bandwidth as the primary path.
© 2026 Lightbits Labs™